3D Human Vision & Graphics
3D human pose estimation and tracking, NeRF-based novel view and pose rendering for human
Creating high-fidelity human avatars is a significant topic in metaverse, AR and VR applications. To achieve this, various solid algorithms are necessary, including 3D human body and pose reconstruction, generation, and realistic rendering. During in Microsoft Research Asia, PI contributed to multiple projects focused on these topics (Gao et al., 2022), (Kim et al., 2023), (Kim et al., 2015).
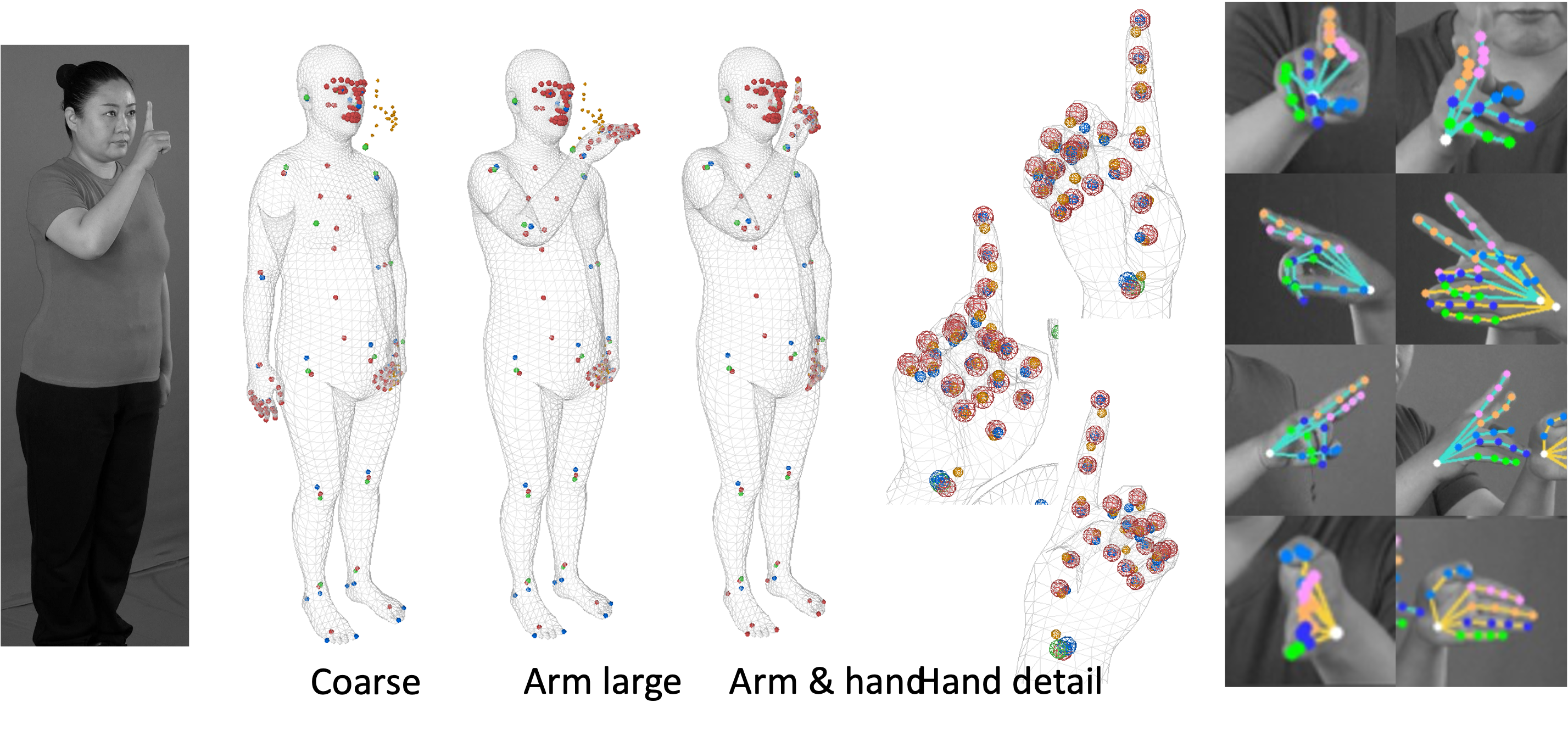
Human pose tracking of sign language videos. Accurate human body and hand pose tracking with weakly synchronized multi-view videos.
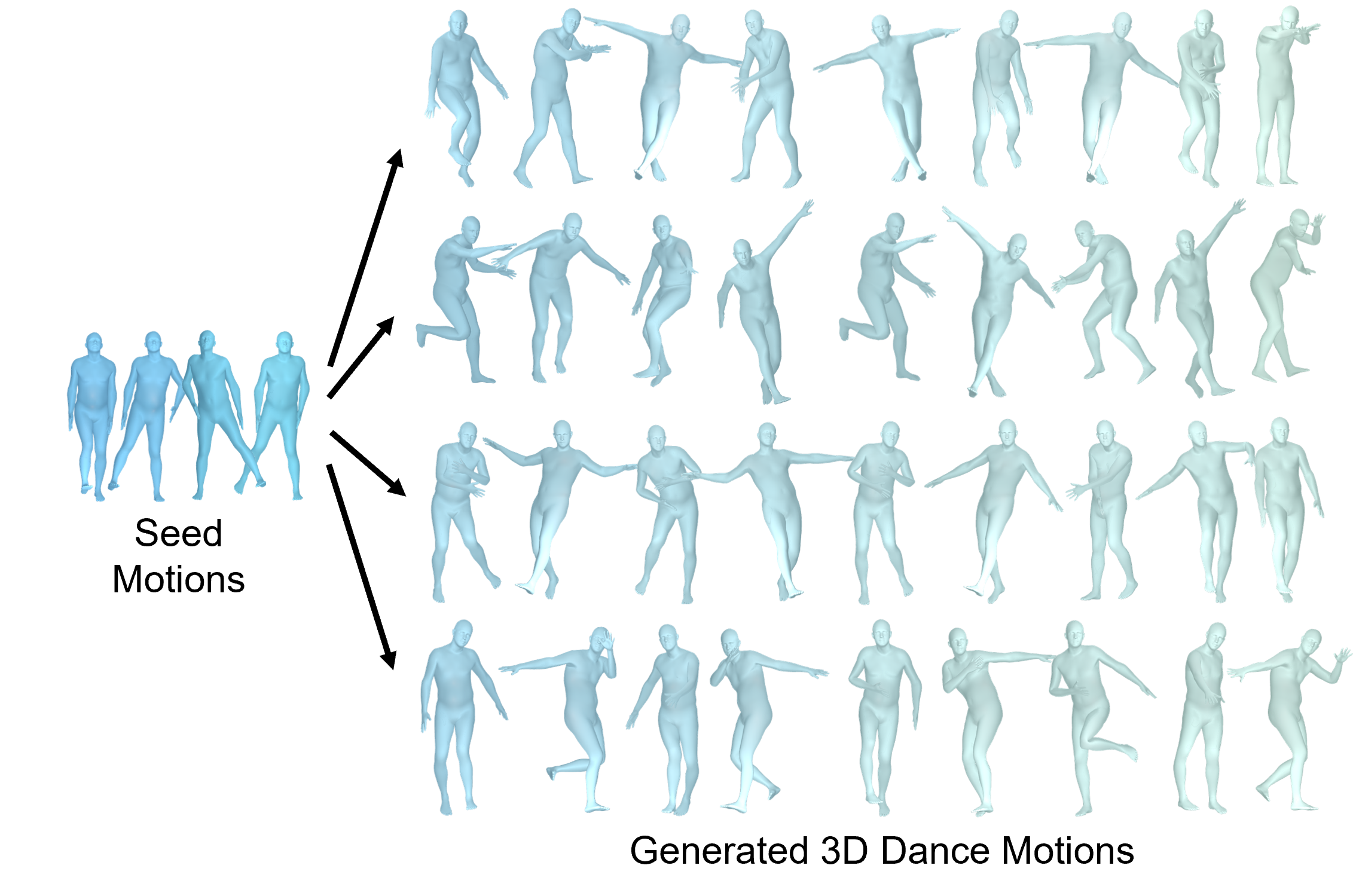

Dance motion generation conditioned on various music sequences.
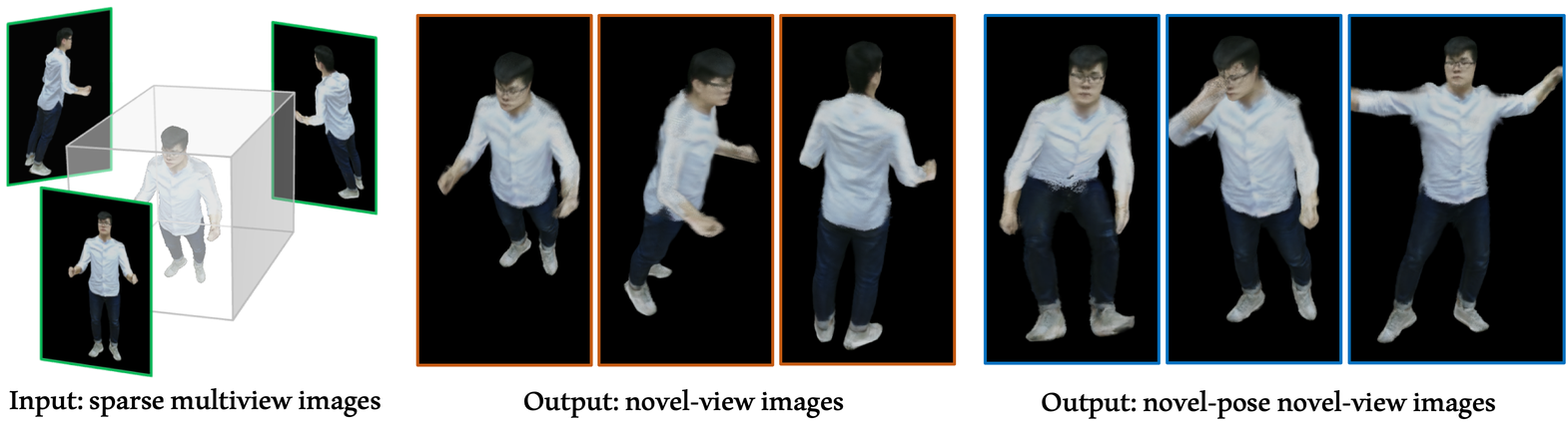
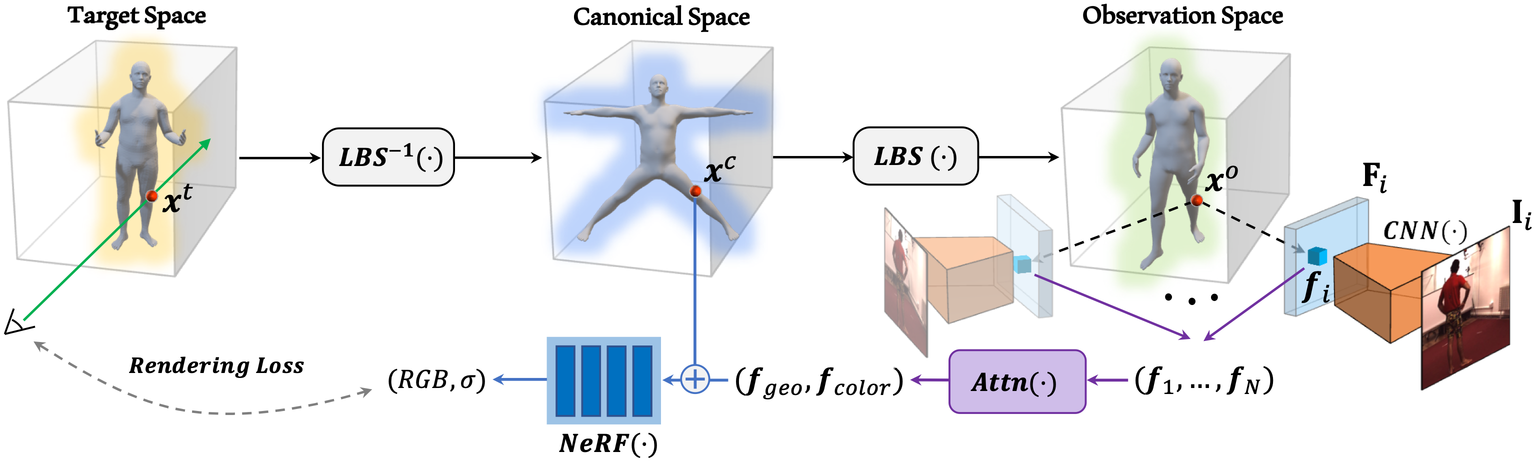

MPS-NeRF. Model & pose agnostic NeRF-based human rendering.
MPS-NeRF demo videos